5.9 Buffer
A buffer is a type of solution that can resist a change in pH.
A solution designed to maintain a constant pH when small amounts of a strong acid or base are added. Buffers usually consist of a fairly weak acid and its salt with a strong base. Suitable concentrations are chosen so that the pH of the solution remains close to the pKa of the weak acid. – CRC 2016
It is able to do this due to the presence of appreciable and similar amounts of acid and conjugate base (or base and conjugate acid) in the same solution. Clearly, for an acid or a base to exist in water, the acid or base must be weak. Similar amounts means the ratio of acid to conjugate base (or base to conjugate acid) must be a 10:1 or 1:10 ratio.
pH of a Buffer Solution
The pH or pOH of a buffer solution can be determined using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
For a buffer made from acid
\[\mathrm{pH} = \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{A^-}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{HA}]}}\]
and a buffer made from a base
\[\mathrm{pOH} = \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{b}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{green}{HB^+}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{red}{B}]}}\]
Creating a Buffer
A buffer solution can be made from
- A weak acid and a salt containing its conjugate base
- A weak acid and a strong base
- A weak base and a salt containing its conjugate acid
- A weak base and a strong acid
But what about a…
…buffer from a Strong Acid or Base?
Given that a buffer must contain both acid and its conjugate base, a buffer cannot be created from a strong acid (since a strong acid nearly completely converts into hydronium).
Consider a 0.1 M HCl aqueous solution (at 25 °C).
Ka(HCl) = 2 × 106
| HCl(aq) | + | H2O(l) | ⇌ | H3O+(aq) | + | Cl–(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
0.1 |
~0 |
0 | ||||
C |
-x |
+x |
+x | ||||
E |
0.1-x |
x |
x |
Solve for x in the equilibrium expression.
\[\begin{align*} \dfrac{[\mathrm{H_3O^+}][\mathrm{Cl^-}]}{[\mathrm{HCl}]} &= K_{\mathrm{a}} \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x^2}{0.1-x} &= 2\times 10^{6} \\[1.5ex] x^2 &= 2\times 10^{6} (0.1-x) \\[1.5ex] &= 2\times 10^{5} - 2\times 10^{6}x\\[1.5ex] x^2 + 2\times 10^{6}x - 2\times 10^{5} &= 0 \\[1.5ex] x &= 0.1 \end{align*}\]
See quadratic solution at WolframAlpha.
The equilibrium concentrations are
\[\begin{align*} [\mathrm{HCl}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 0~M \\ [\mathrm{H_3O^+}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 0.1~M\\ [\mathrm{Cl^-}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 0.1~M \end{align*}\]
The amount of strong acid, HCl, at equilibrium is zero. Therefore, the acid-to-base ratio is zero and the solution is not a buffer!
Buffers cannot be created from strong acids or strong bases!
…buffer from only a Weak Acid?
Let us consider the weak acid, acetic acid (CH3COOH), and create a 0.01 M aqueous solution. The Ka = 1.75 × 10–5. Solve for the equilibrium concentrations.
| CH3COOH(aq) | + | H2O(l) | ⇌ | H3O+(aq) | + | CH3COO–(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
0.01 |
~0 |
0 | ||||
C |
-x |
+x |
+x | ||||
E |
0.01 - x |
x |
x |
\[\begin{align*} \dfrac{[\mathrm{H_3O^+}][\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} &= K \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x^2}{0.01-x} &= 1.75\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x^2}{0.01} &= 1.75\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] x^2 &= 1.75\times 10^{-7} \\[1.5ex] x &= 4.18\times 10^{-4} \quad (4.18\%) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} [\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 9.58\times 10^{-3} \\ [\mathrm{H_3O^+}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 4.18\times 10^{-4}\\ [\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 4.18\times 10^{-4} \end{align*}\]
Our weak acid solution contains both weak acid (CH3COOH) and conjugate base (CH3COO–). Let us determine the ratio and ensure it fits our definition of a buffer.
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} = \dfrac{4.18\times 10^{-4}}{9.58\times 10^{-3}} = 0.04\] or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]} = \dfrac{9.58\times 10^{-5}}{4.18\times 10^{-4}} = 22.9\]
The ratio of acid to base lies outside the range of 0.1 to 10. A 0.01 M CH3COOH aqueous solution is not a buffer.
…buffer from only a Weak Base?
Let us consider the weak base, ammonia (NH3), and create a 0.01 M aqueous solution. The Kb(NH3) = 1.77 × 10–5. Solve for the equilibrium concentrations.
| NH3(aq) | + | H2O(l) | ⇌ | OH–(aq) | + | NH4+(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
0.01 |
~0 |
0 | ||||
C |
-x |
+x |
+x | ||||
E |
0.01 - x |
x |
x |
\[\begin{align*} \dfrac{[\mathrm{OH^-}][\mathrm{NH_4^+}]}{[\mathrm{NH_3}]} &= K \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x^2}{0.01-x} &= 1.77\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x^2}{0.01} &= 1.77\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] x^2 &= 1.77\times 10^{-7} \\[1.5ex] x &= 4.21\times 10^{-4} \quad (4.21\%) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} [\mathrm{NH_3}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 1.96\times 10^{-2}~M \\ [\mathrm{OH^-}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 4.21\times 10^{-4}~M\\ [\mathrm{NH_4^+}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 4.21\times 10^{-4}~M \end{align*}\]
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]}{[\mathrm{NH_3}]} = \dfrac{4.21\times 10^{-4}}{1.96\times 10^{-2}} = 0.02\]
or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_3}]}{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]} = \dfrac{1.96\times 10^{-2}}{4.21\times 10^{-4}} = 46.5\]
A 0.01 M NH3 aqueous solution is not a buffer.
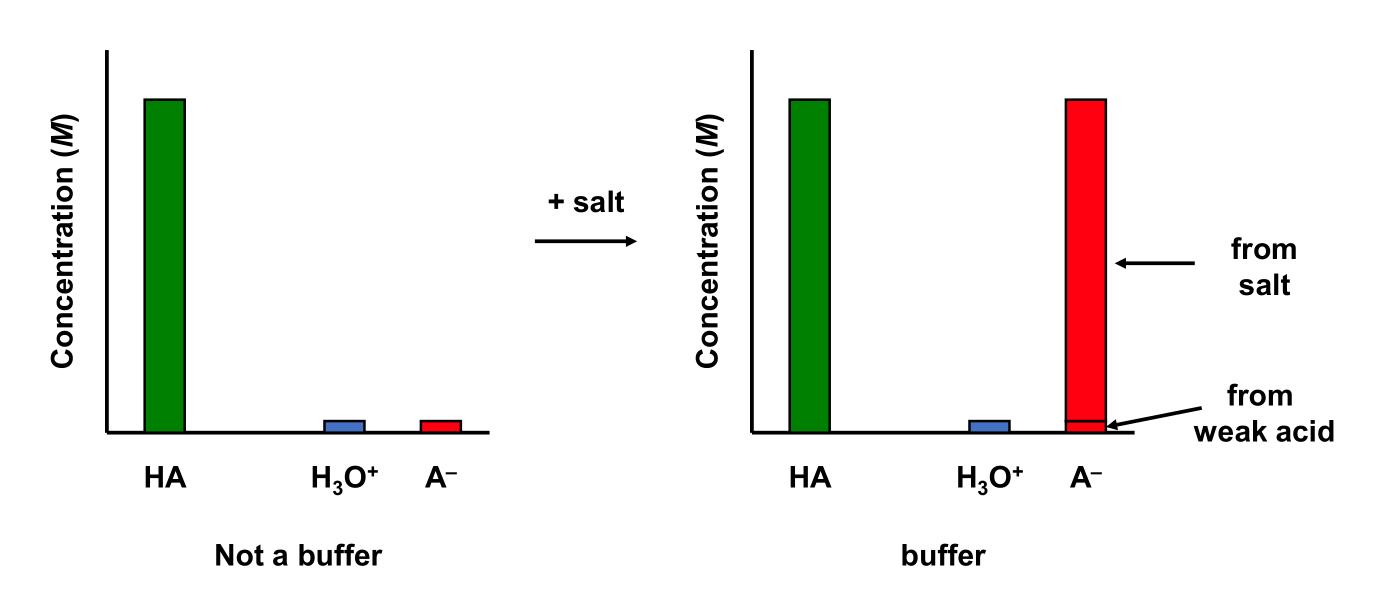
5.9.1 Weak Acid and Salt
Consider a 0.01 M acetic acid (CH3COOH) aqueous solution containing 0.01 M sodium acetate (NaCH3COO). Ka = 1.75 × 10–5
This solution contains a weak acid and a salt containing the conjugate base to the weak acid. Determine the equilibrium concentrations of the weak acid and conjugate base.
Work
Full Version
| CH3COOH(aq) | + | H2O(l) | ⇌ | H3O+(aq) | + | CH3COO–(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
0.01 |
~0 |
0.01 | ||||
C |
-x |
+x |
+x | ||||
E |
0.01 - x |
x |
0.01+x |
\[\begin{align*} \dfrac{[\mathrm{H_3O^+}][\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} &= K \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x(0.01+x)}{0.01-x} &= 1.75\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{0.01x}{0.01} &= 1.75\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] 0.01x &= 1.75\times 10^{-7} \\[1.5ex] x &= 1.75\times 10^{-5} \quad (0.18\%) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} [\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 9.98\times 10^{-3} \\ [\mathrm{H_3O^+}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 1.75\times 10^{-5}\\ [\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 1.00\times 10^{-2} \end{align*}\]
The ratio of acid to base is
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} = \dfrac{1.00\times 10^{-2}}{9.98\times 10^{-3}} = 1.002\] or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]} = \dfrac{9.98\times 10^{-3}}{1.00\times 10^{-2}} = 0.998\]
The ratio lies between the range of 0.1 to 10. Therefore, this solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an acid) to determine the pH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{A^-}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{HA}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.75\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{1.00\times 10^{-2}~M}{9.98\times 10^{-3}~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.76 \end{align*}\]
Short Version
Skip the ICE table and simply approximate the equilibrium concentrations of the weak acid, HA, and conjugate base, A– to both be 0.01 M.
The ratio of acid to conjugate base lies between the range of 0.1 to 10 (it is exactly 1 in this example). Therefore, this solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an acid) to determine the pH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{A^-}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{HA}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.75\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{0.01~M}{0.01~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.76 \end{align*}\]
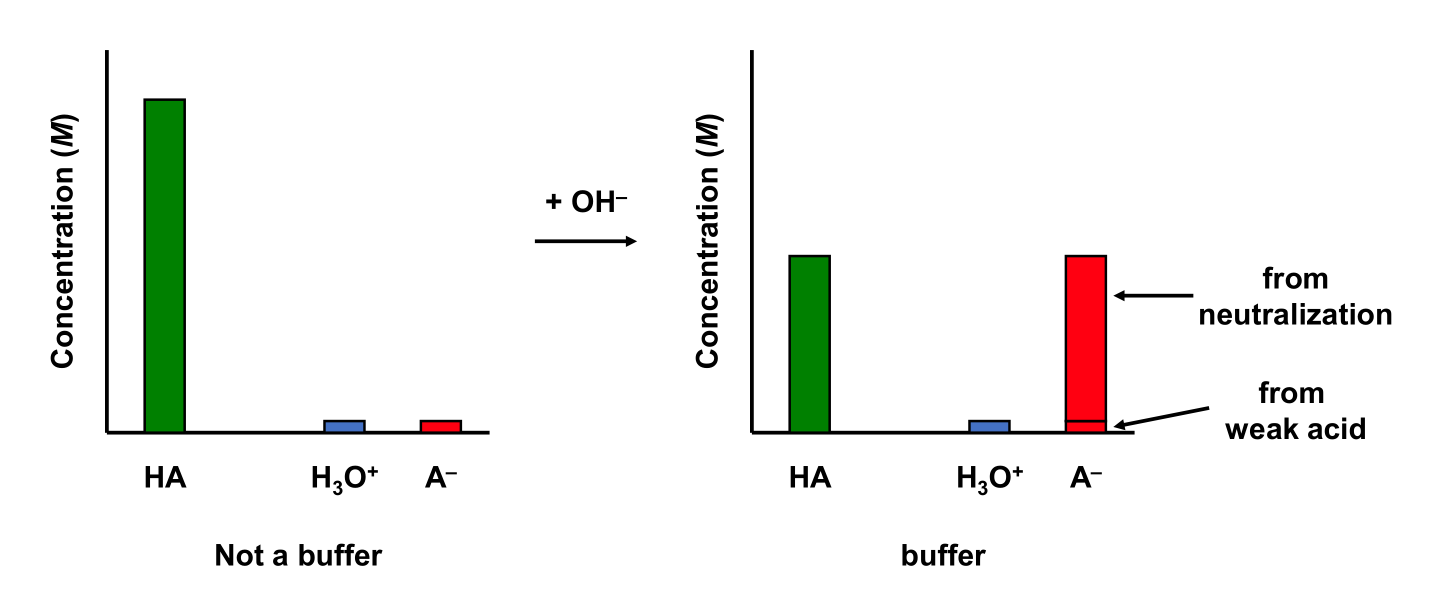
5.9.2 Weak Acid and Strong Base
Adding some strong base to a weak acid solution can create a buffer because an acid-base neutralization reaction will take place to consume weak acid and produce conjugate base.
\[\mathrm{HA}(aq) + \mathrm{OH^-}(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{A^-}(aq)\]
Consider a 50.0 mL 0.01 M acetic acid (CH3COOH; Ka = 1.75 × 10–5) aqueous solution. Add 10.00 mL 0.01 M NaOH to the solution. The solution is a buffer!
Note: This type of problem introduces a new component to the procedure for solving. Analyze carefully.
Work
To solve this type of problem, we will first consider the acid-base neutralization reaction that is to take place. A strong base, OH– (from NaOH), is added to a weak acid solution. The added base will react with the weak acid in solution such that
\[\mathrm{HA}(aq) + \mathrm{OH^-}(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{A^-}(aq)\]
We treat this reaction as a limiting reactant type problem. Therefore, we must convert everything to moles and carry out the reaction.
\[\begin{align*} n_{\mathrm{HA}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~HA} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{OH}^{-}} &= (0.01~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0001~\mathrm{mol~OH}^{-} \end{align*}\]
Next, write out an IRF table (I = initial moles, R = reaction, F = final moles) and run the reaction to completion.
I |
0.0005 |
0.0001 |
0 | ||||
R |
HA |
+ |
OH– |
→ |
H2O |
+ |
A– |
F |
0.0004 |
0 |
0.0001 |
Here, the strong base is the limiting reactant.
Next, convert everything back to molarity. Note that the volume of the solution has increased since we added some strong base (10.0 mL) to the starting solution (50.0 mL)!
\[\begin{align*} V_{\mathrm{final}} &= 50.0~\mathrm{mL} + 10.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 60.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 0.0600~\mathrm{L} \\[2ex] [\mathrm{HA}] &= \dfrac{0.0004~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00667~M \\[1.5ex] [\mathrm{A^-}] &= \dfrac{0.0001~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00167~M \end{align*}\]
We can stop here and determine if we have a buffer. The ratio of acid to base is
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} = \dfrac{1.67\times 10^{-3}}{6.67\times 10^{-3}} = 0.250\] or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]} = \dfrac{6.67\times 10^{-3}}{1.67\times 10^{-3}} = 3.99\] Since the ratio of acid to base lies between 0.1 and 10, this solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an acid) to determine the pH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{A^-}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{HA}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.75\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{0.00167~M}{0.00667~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.16 \end{align*}\]
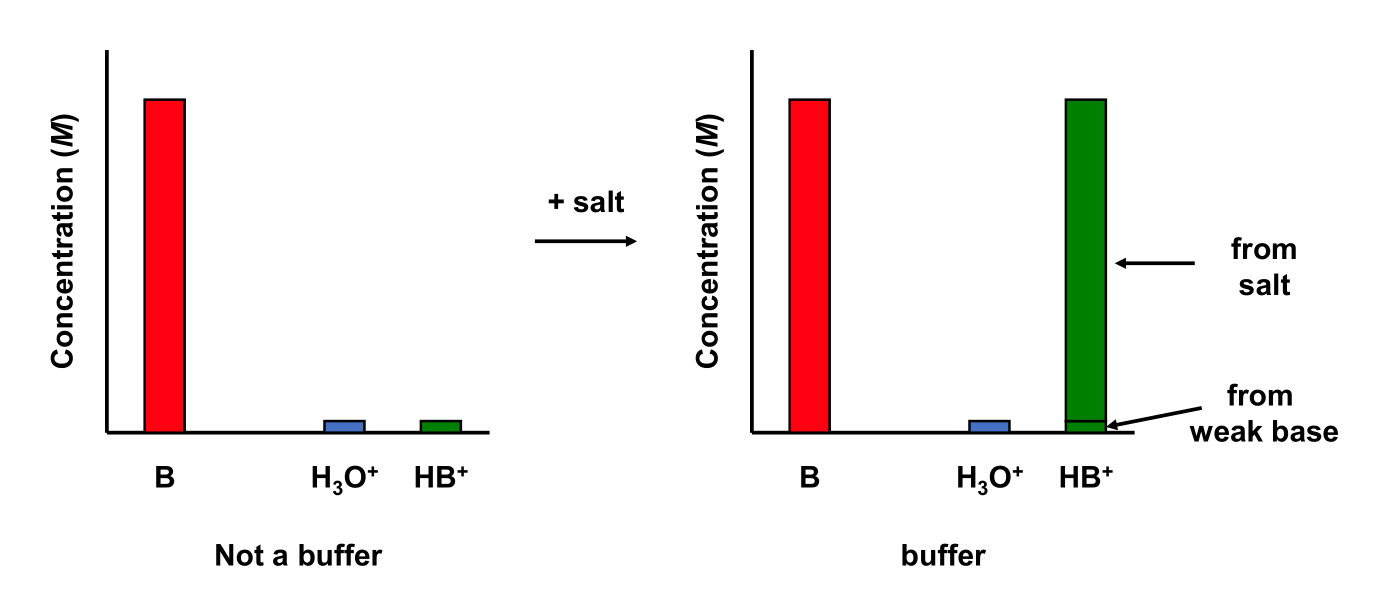
5.9.3 Weak Base and Salt
Consider a 0.01 M ammonia (NH3; Kb(NH3) = 1.77 × 10–5) aqueous solution containing 0.01 M ammonium chloride (NH4Cl).
This solution contains a weak base and a salt containing the conjugate acid to the weak base Determine the equilibrium concentrations of the weak base and conjugate acid
Work
Long Version
| NH3(aq) | + | H2O(l) | ⇌ | OH–(aq) | + | NH4+(aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
0.01 |
~0 |
0.01 | ||||
C |
-x |
+x |
+x | ||||
E |
0.01 - x |
x |
0.01+x |
\[\begin{align*} \dfrac{[\mathrm{OH^-}][\mathrm{NH_4^+}]}{[\mathrm{NH_3}]} &= K \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{x(0.01+x)}{0.01-x} &= 1.77\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] \dfrac{0.01x}{0.01} &= 1.77\times 10^{-5} \\[1.5ex] 0.01x &= 1.77\times 10^{-7} \\[1.5ex] x &= 1.77\times 10^{-5} \quad (0.18\%) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*} [\mathrm{NH_3}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 9.98\times 10^{-3}~M \\ [\mathrm{OH^-}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 1.77\times 10^{-5}~M\\ [\mathrm{NH_4^+}]_{\mathrm{eq}} &= 1.00\times 10^{-2}~M \end{align*}\]
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]}{[\mathrm{NH_3}]} = \dfrac{1.00\times 10^{-2}}{9.98\times 10^{-3}} = 1.00\]
or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_3}]}{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]} = \dfrac{9.98\times 10^{-3}}{1.00\times 10^{-2}} = 0.998\]
This solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an base) to determine the pOH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pOH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{b}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{HB^+}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{B}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.77\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{1.00\times 10^{-2}~M}{9.98\times 10^{-3}~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.75 \end{align*}\]
Find the pH (at 25 °C).
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{w}} - \mathrm{pOH} \\[1.5ex] &= 14 - 4.75 \\[1.5ex] &= 9.25 \end{align*}\]
Short Version
Skip the ICE table and simply approximate the equilibrium concentrations of the weak acid, B, and conjugate base, HB+ to both be 0.01 M.
The ratio of base to conjugate acid lies between the range of 0.1 to 10 (it is exactly 1 in this example). Therefore, this solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an base) to determine the pH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pOH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{b}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{HB^+}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{B}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.77\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{0.01~M}{0.01~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.75 \end{align*}\]
Find the pH (at 25 °C).
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{w}} - \mathrm{pOH} \\[1.5ex] &= 14 - 4.76 \\[1.5ex] &= 9.25 \end{align*}\]
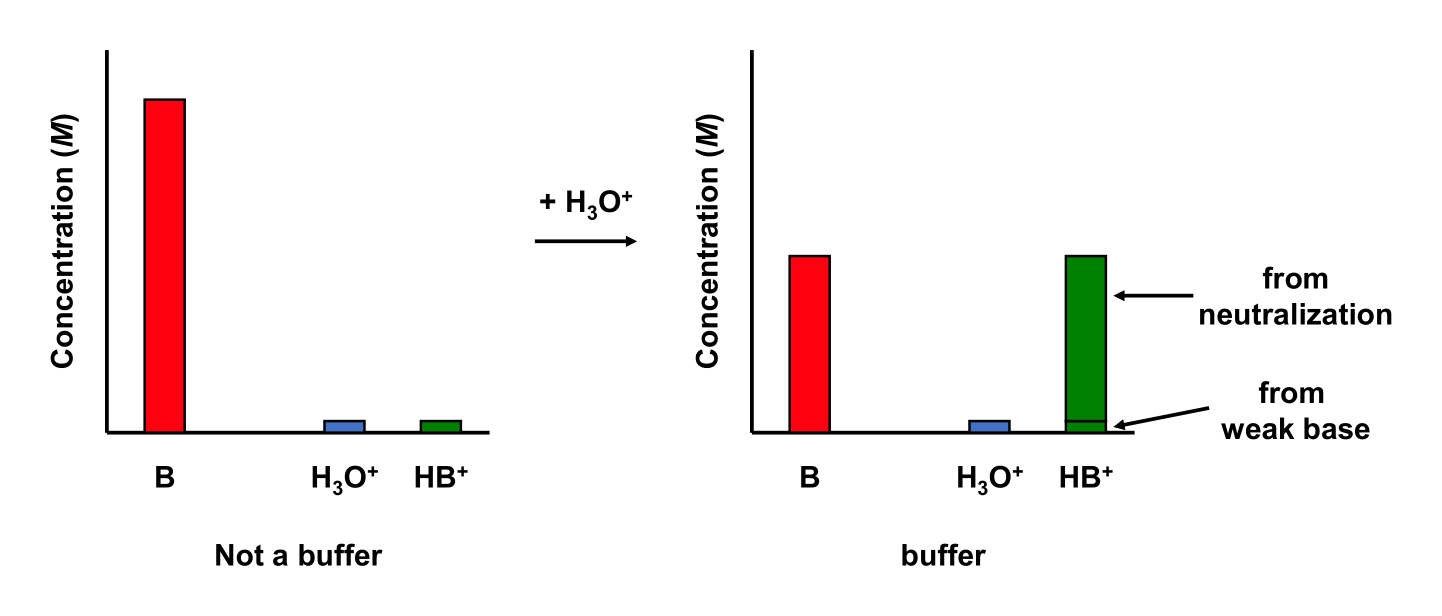
5.9.4 Weak Base and Strong Acid
Adding some strong acid to a weak base solution can create a buffer because an acid-base neutralization reaction will take place to consume weak base and produce conjugate acid.
\[\mathrm{B}(aq) + \mathrm{H_3O^+}(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{HB^+}(aq)\]
Consider a 50.0 mL 0.01 M ammonia (NH3; Kb = 1.77 × 10–5) aqueous solution. Add 10.00 mL 0.01 M HCl to the solution. The solution is a buffer!
Note: This type of problem introduces a new component to the procedure for solving. Analyze carefully.
Work
To solve this type of problem, we will first consider the acid-base neutralization reaction that is to take place. A strong base, H3O+ (from HCl), is added to a weak base solution. The added acid will react with the weak base in solution such that
\[\mathrm{B}(aq) + \mathrm{H_3O^+}(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{HB^+}(aq)\]
We treat this reaction as a limiting reactant type problem. Therefore, we must convert everything to moles and carry out the reaction.
\[\begin{align*} n_{\mathrm{B}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~B} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{H_3O}^{+}} &= (0.01~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0001~\mathrm{mol~H_3O}^{+} \end{align*}\]
Next, write out an IRF table (I = initial moles, R = reaction, F = final moles) and run the reaction to completion.
I |
0.0005 |
0.0001 |
0 | ||||
R |
B |
+ |
H3O+ |
→ |
H2O |
+ |
HB+ |
F |
0.0004 |
0 |
0.0001 |
Here, the strong acid is the limiting reactant.
Next, convert everything back to molarity. Note that the volume of the solution has increased since we added some strong base (10.0 mL) to the starting solution (50.0 mL)!
\[\begin{align*} V_{\mathrm{final}} &= 50.0~\mathrm{mL} + 10.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 60.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 0.0600~\mathrm{L} \\[2ex] [\mathrm{B}] &= \dfrac{0.0004~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00667~M \\[1.5ex] [\mathrm{HB^+}] &= \dfrac{0.0001~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00167~M \end{align*}\]
We can stop here and determine if we have a buffer. The ratio of acid to base is
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{acid}]}{[\mathrm{base}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]}{[\mathrm{NH_3}]} = \dfrac{1.67\times 10^{-3}}{6.67\times 10^{-3}} = 0.250\]
or
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{NH_3}]}{[\mathrm{NH_4^+}]} = \dfrac{6.67\times 10^{-3}}{1.67\times 10^{-3}} = 3.99\]
Since the ratio of acid to base lies between 0.1 and 10, this solution is a buffer!
Use Henderson-Hasselbalch (for a buffer made from an base) to determine the pH.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pOH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{b}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{\color{red}{HB^+}}]}{\mathrm{[\color{green}{B}]}} \\[1.5ex] &= -\log (1.77\times 10^{-5}) + \log\dfrac{1.67\times 10^{-3}~M}{6.67\times 10^{-3}~M}\\[1.5ex] &= 4.15 \end{align*}\]
Find the pH (at 25 °C).
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{w}} - \mathrm{pOH} \\[1.5ex] &= 14 - 4.15 \\[1.5ex] &= 9.85 \end{align*}\]
5.9.5 Resisting a change in pH
A buffer contains both acid and base. When adding an acid to the buffer solution, the added acid can react with the base in the buffer. This effectively helps neutralize the added acid! Since the added acid is neutralized (to produce water and a salt), the change in pH is small.
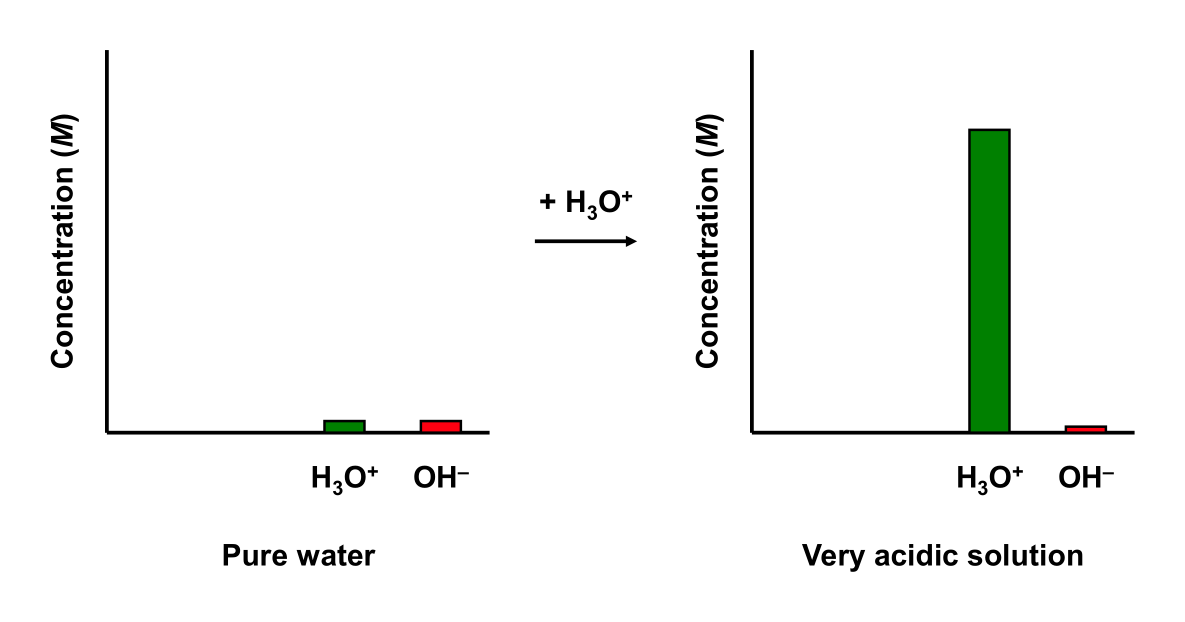
Water has no buffering capability. Adding a strong acid to water dramatically changes its pH.
pH change of Strong Acid + Water
Add enough HCl to pure water (at 25 °C) to make a 0.01 M solution. Water initial has a pH of 7. Upon addition of the acid, the pH of the solution is 2. Water experiences a ΔpH = –5.
An acidic buffer has some buffering capability. Adding a strong acid to an acidic buffer will affect its pH slightly.
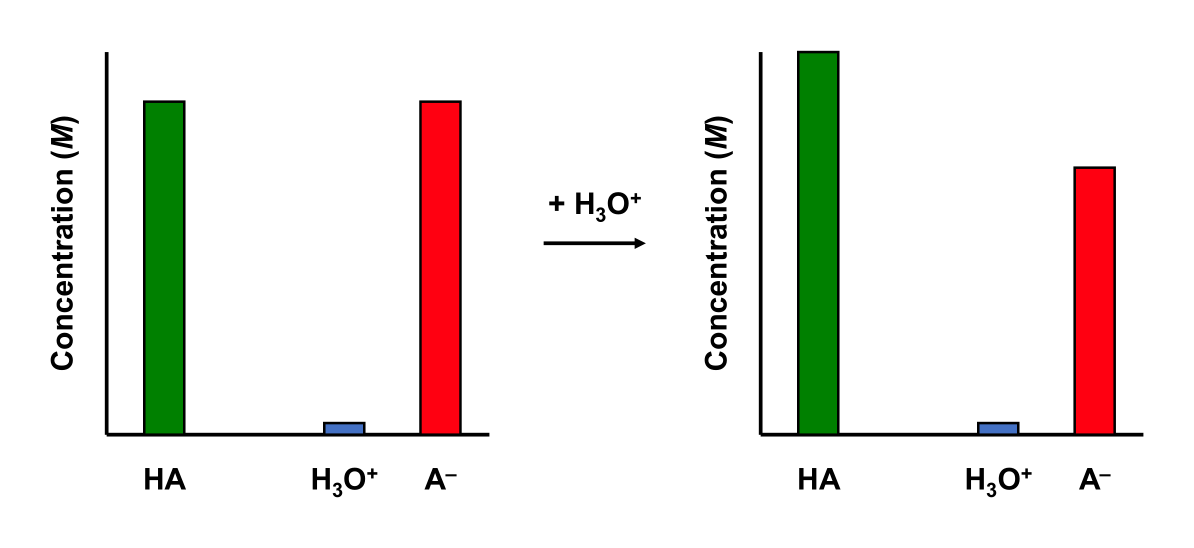
pH change of Strong Acid + Acidic Buffer
Add 10.0 mL 0.01 M HCl to a 50.0 mL buffer containing 0.01 M CH3COOH (Ka = 1.75 ×10–5) and 0.01 M NaCH3COO aqueous solution (at 25 °C). The solution initially has a pH of 4.76.
The added acid, H3O+, will react with the base that is in solution, CH3COO–.
\[\mathrm{A^-}(aq) + \mathrm{H_3O^+}(aq) \longrightarrow \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{HA}(aq) \]
Convert everything to moles.
\[\begin{align*} n_{\mathrm{HA}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~HA} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{A^-}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~A^-} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{H_3O^+}^{-}} &= (0.01~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0001~\mathrm{mol~H_3O^+} \end{align*}\]
I |
0.0005 |
0.0001 |
0.0005 | ||||
R |
A– |
+ |
H3O+ |
→ |
H2O |
+ |
HA |
F |
0.0004 |
0 |
0.0006 |
Convert back to molarity.
\[\begin{align*} V_{\mathrm{final}} &= 50.0~\mathrm{mL} + 10.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 60.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 0.0600~\mathrm{L} \\[2ex] [\mathrm{HA}] &= \dfrac{0.0006~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.01~M \\[1.5ex] [\mathrm{A^-}] &= \dfrac{0.0004~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00667~M \\[1.5ex] \end{align*}\]
We still have a buffer.
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} = \dfrac{6.67\times 10^{-3}}{0.01} = 1.50\]
Solve for pH using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{A^-}]}{\mathrm{[HA]}}\\[1.5ex] &= \mathrm{-\log(1.75\times 10^{-5})} + \log\dfrac{6.67\times 10^{-3}}{0.01} \\[1.5ex] &= 4.58 \end{align*}\]
The buffer solution experienced a pH change of only 0.18.
Similarly, adding a base to a buffer solution will cause an acid-base neutralization reaction. The added base will react with the acid in the buffer solution to produce water and a salt. The resulting pH change is small.
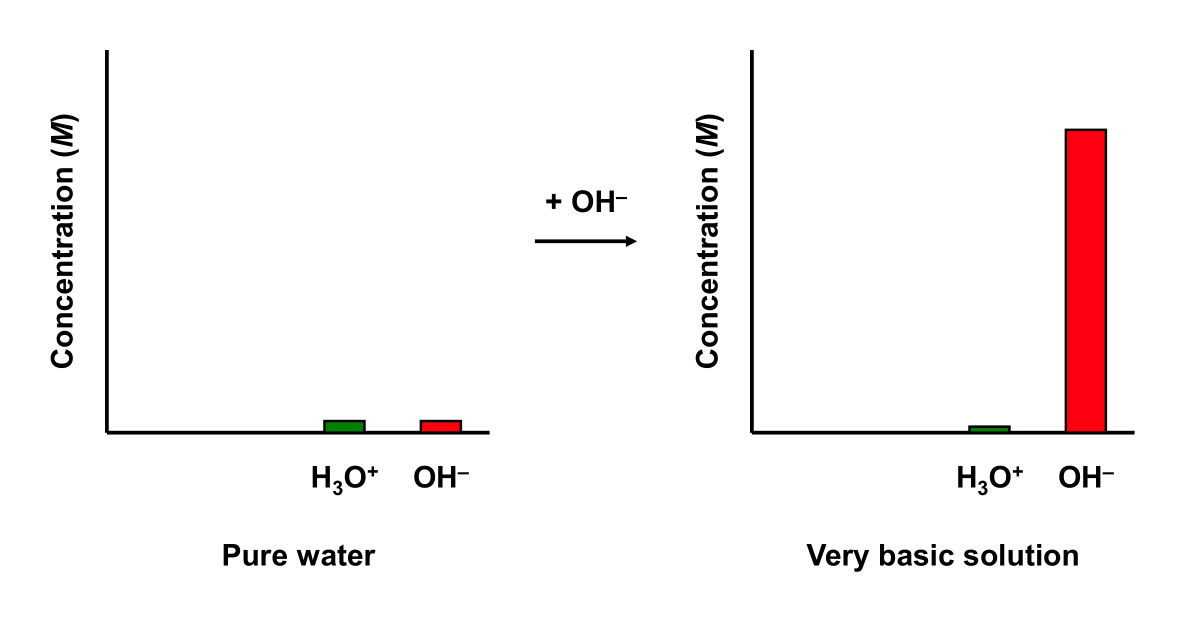
Water has no buffering capability. Adding a strong base to water dramatically changes its pH.
pH change of Strong Base + Water
Add enough NaOH to pure water (at 25 °C) to make a 0.01 M solution. Water initial has a pH of 7. Upon addition of the base, the pH of the solution is 12. Water experiences a ΔpH = 5.
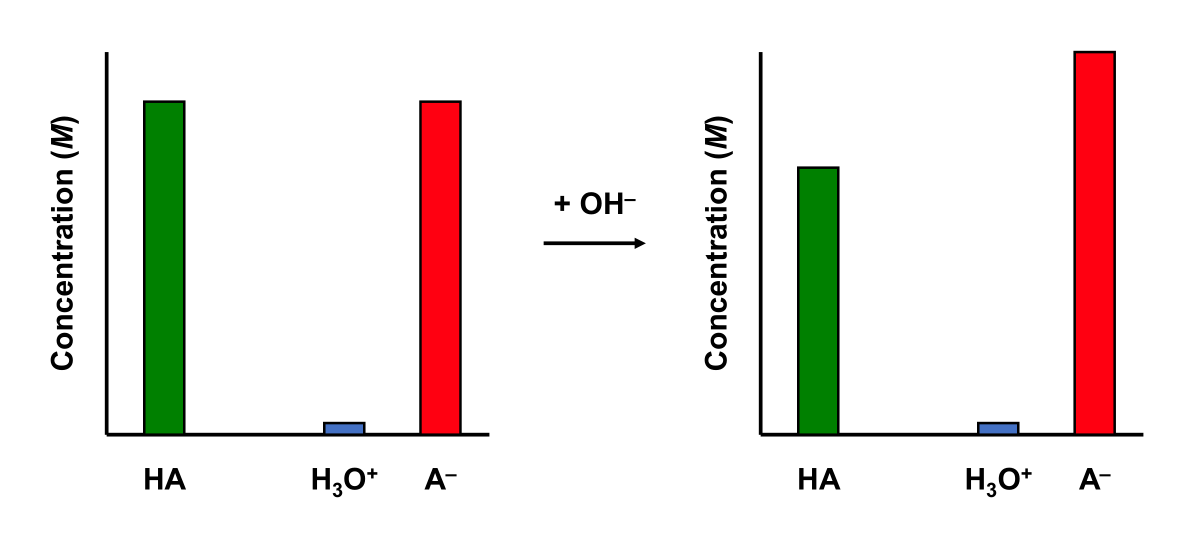
A basic buffer has some buffering capability. Adding a strong base to an basic buffer will affect its pH slightly.
pH change of Strong Base + Acidic Buffer
Add 10.0 mL 0.01 M NaOH to a 50.0 mL buffer containing 0.01 M CH3COOH (Ka = 1.75 ×10–5) and 0.01 M NaCH3COO aqueous solution (at 25 °C). The solution initially has a pH of 4.76.
The added base, OH–, will react with the acid that is in solution, CH3COOH.
\[\mathrm{HA}(aq) + \mathrm{OH^-}(aq) \longrightarrow \mathrm{H_2O}(l) + \mathrm{A^-}(aq) \]
Convert everything to moles.
\[\begin{align*} n_{\mathrm{HA}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~HA} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{A^-}} &= (0.050~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0005~\mathrm{mol~A^-} \\[2ex] n_{\mathrm{OH}^{-}} &= (0.01~\mathrm{L})\left(0.01~\mathrm{mol~L}^{-1}\right)\\ &= 0.0001~\mathrm{mol~OH}^{-} \end{align*}\]
I |
0.0005 |
0.0001 |
0.0005 | ||||
R |
HA |
+ |
OH– |
→ |
H2O |
+ |
A– |
F |
0.0004 |
0 |
0.0006 |
Convert back to molarity.
\[\begin{align*} V_{\mathrm{final}} &= 50.0~\mathrm{mL} + 10.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 60.0~\mathrm{mL} \\ &= 0.0600~\mathrm{L} \\[2ex] [\mathrm{HA}] &= \dfrac{0.0004~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.00667~M \\[1.5ex] [\mathrm{A^-}] &= \dfrac{0.0006~\mathrm{mol}}{0.0600~\mathrm{L}}\\[1.5ex] &= 0.01~M \end{align*}\]
We still have a buffer.
\[\dfrac{[\mathrm{base}]}{[\mathrm{acid}]} = \dfrac{[\mathrm{CH_3COO^-}]}{[\mathrm{CH_3COOH}]} = \dfrac{0.01}{6.67\times 10^{-3}} = 1.50\]
Solve for pH using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{pH} &= \mathrm{p}K_{\mathrm{a}} + \log\dfrac{[\mathrm{A^-}]}{\mathrm{[HA]}}\\[1.5ex] &= \mathrm{-\log(1.75\times 10^{-5})} + \log\dfrac{0.01}{6.67\times 10^{-3}} \\[1.5ex] &= 4.93 \end{align*}\]
The buffer solution experienced a pH change of only 0.17.
5.9.6 Buffer Capacity
Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base a buffer is able to neutralize. Buffers containing higher concentrations of acid/c.base or base/c.acid have a larger buffering capacity.
Practice
Which buffer has a larger buffer capacity?
- 0.001 M CH3COOH + 0.001 M NaCH3COO
- 0.1 M CH3COOH + 0.1 M NaCH3COO
Solution
The second buffer