1.11 Practice Problems
Attempt these problems as if they were real exam questions in an exam environment.
Only look up information if you get severely stuck. Never look at the solution until you have exhausted all efforts to solve the problem. Having to look up information or the solution should be an indicator that the previous layers (1–5) in the Structured Learning Approach have not been mastered.
Which of the following n–alkanes has the highest boiling point?
- C5H12
- C7H16
- C4H10
- C9H20
- C3H8
Solution
Answer: D
Concept: Intermolecular forces and structure
The strength of intermolecular forces can affect the boiling points of a substance. Stronger IMFs generally lead to larger boiling points.
Given is a list of hydrocarbons which predominantly exhibit dispersion. Dispersion increases with molecule size. Therefore, the largest molecule in this series exhibts the most dispersion and, therefore, is expected to have the highest boiling point.
What word describes the phase transition from the liquid to the gas phase?
- sublimation
- fusion
- condensation
- vaporization
- none of these
Solution
Answer: D
Concept: Phase transitions
Which of the following is considered to be an endothermic process?
- fusion
- condensation
- deposition
- freezing
- none of these
Solution
Answer: A
Concept: Phase transitions
Fusion (also known as melting) requires an input of thermal energy (endothermic).
Predict the state of an unknown substance if the temperature was significantly decreased and the pressure was significantly increased.
- solid
- liquid
- gas
Solution
Answer: A
Concept: Phase diagram
Generally, decreasing temperature of a substance results in a gas → liquid → solid.
Generally, increasing pressure of a substance results in a gas → liquid → solid.
The heat of vaporization for water at 100 °C is 40.7 kJ mol–1. What is the heat of vaporization (in kJ mol–1) for water at 25 °C?
- exactly –40.7
- greater than 40.7
- equal to 40.7
- less than 40.7
- none of these
Solution
Answer: B
Concept: Heat/Enthalpy of vaporization
The heat of vaporization for a substance increases with decreasing temperature.
According to Hess’s Law, the enthalpy of sublimation can be approximated by adding which two terms together?
- ΔHfrz + ΔHdep
- ΔHfrz + ΔHvap
- ΔHsub + ΔHdep
- ΔHfus + ΔHvap
- none of these
Solution
Answer: D
Concept: Phase transitions
A subtance heated from a solid to a gas sometimes melts (\(\Delta H_{\mathrm{fus}}\)) and then vaporizes (\(\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}\)). Sublimation can be approximated as the the addition of these two terms.
\[\Delta H_{\mathrm{sub}} \approx \Delta H_{\mathrm{fus}} + \Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}\]
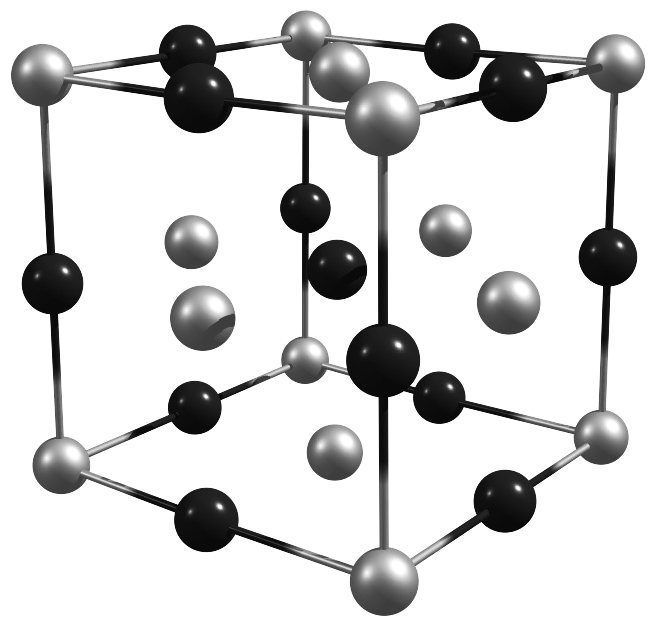
What is the empirical formula of the unit cell for a binary ionic compound shown on the cover of this exam? (A = black particles, X = gray particles).
- A3X
- A13X14
- AX
- A2X4
- A4X4
Solution
Answer: C
Concept: Unit cells and equivalent atoms
Corners = 1/8
Edges = 1/4
Faces = 1/2
Inside = 1Number of equivalent atoms
\[\begin{align*} \mathrm{eq.~A~particles} &= \dfrac{1}{4} ~\left ( \mathrm{12~edge~particles} \right ) + \left( \mathrm{1~particle~inside} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= 4~\mathrm{A~particles} \\[2.5ex] \mathrm{eq.~X~particles} &= \dfrac{1}{8} ~\left ( \mathrm{8~corner~particles} \right ) + \dfrac{1}{2} ~\left ( \mathrm{6~face~particles} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= 4~\mathrm{X~particles} \end{align*}\]
Determine empirical formula
\[\mathrm{A_4X_4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{AX}\]
How much liquid water (in L) at 100 °C can be theoretically vaporized when 30,000 kJ worth of heat is absorbed? Assume water has a density of 1.0 g mL–1. ΔHvap(H2O) = 43.46 kJ mol–1
- 12.44
- 1.24 × 104
- 3.12 × 10–3
- 0.13
- 4.6 × 102
Solution
Answer: A
Concept: Heat/Enthalpy of vaporization
Enthalpy is an extensive property.
Moles of water that can be vaporized
\[\begin{align*} q &= n\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}} \longrightarrow \\[1.5ex] n &= \dfrac{q}{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}} \\[1.5ex] &= \dfrac{3.0\times 10^4~\mathrm{kJ}}{43.46~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}}} \\[1.5ex] &= 690.289~\mathrm{mol~H_2O} \end{align*}\]
Moles to mass (in g)
\[\begin{align*} m &= n \times \text{molar mass} \\[1.5ex] &= 690.289~\mathrm{mol} \left ( \dfrac{18.02~\mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{mol}} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= 12,439.01~\mathrm{g} \end{align*}\]
Mass to volume (in L)
\[\begin{align*} d &= \dfrac{m}{V} \longrightarrow \\[1.5ex] V &= \dfrac{m}{d} \\[1.5ex] &= \left ( \dfrac{12,439.01~\mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{1.0~g~mL^{-1}}} \right ) \left ( \dfrac{1~\mathrm{L}}{10^3~\mathrm{mL}} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= 12.44~\mathrm{L} \end{align*}\]
How much heat is evolved/released (in kJ) when 100 g of 80 °C water is converted into –35 °C ice? This process is carried out at sea level.
csolid = 2.09 J g–1 °C–1, cliquid = 4.184 J g–1 °C–1, cgas = 1.84 J g–1 °C–1
ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ mol–1, ΔHvap = 40.67 kJ mol–1- 24
- 33
- 74
- 105
- 662
Solution
Answer: C
Concept: Heating curve
Recognize that the substance is water so we are expected to know its normal freezing and boiling points. If the substance was not water, these values would be given.
\[\begin{align*} \Delta T_{\mathrm{f}} &= 0~^{\circ}\mathrm{C} \\[1.5ex] \Delta T_{\mathrm{b}} &= 100~^{\circ}\mathrm{C} \end{align*}\]
Next, realize that three regions of the heating curve must be accounted for.
1. Cooling liquid to freezing point 2. Freezing the liquid 3. Cooling the solid to the final temperatureHeat lost when cooling liquid to freezing point
\[\begin{align*} q_1 &= mc_{\mathrm{liquid}}\Delta T \\[1.5ex] &= (100~\mathrm{g})(4.184~\mathrm{J~g^{-1}~^{\circ}C})(0~^{\circ}\mathrm{C} - 80~^{\circ}\mathrm{C}) \left ( \dfrac{1~\mathrm{kJ}}{10^3~\mathrm{J}}\right )\\[1.5ex] &= -33.472~\mathrm{kJ} \end{align*}\]
Heat lost when undergoing freezing
Because water is freezing, ΔHfus = –ΔHfrz. Also, convert mass to moles.
\[\begin{align*} q_2 &= n\Delta H_{\mathrm{frz}} \\[1.5ex] &= \left ( \dfrac{100~\mathrm{g}}{18.02~\mathrm{g~mol^{-1}}} \right ) \left ( -6.01~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= -33.352~\mathrm{kJ} \end{align*}\]
Heat lost when cooling solid to final temperature
\[\begin{align*} q_3 &= mc_{\mathrm{liquid}}\Delta T \\[1.5ex] &= (100~\mathrm{g})(2.09~\mathrm{J~g^{-1}~^{\circ}C})(-35~^{\circ}\mathrm{C} - 0~^{\circ}\mathrm{C}) \left ( \dfrac{1~\mathrm{kJ}}{10^3~\mathrm{J}}\right )\\[1.5ex] &= -7.315~\mathrm{kJ} \end{align*}\]
Total heat lost
\[\begin{align*} q_{\mathrm{tot}} &= q_1 + q_2 + q_3 \\[1.5ex] &= -33.472~\mathrm{kJ} + -33.352~\mathrm{kJ} + -7.315~\mathrm{kJ} \\[1.5ex] &= -74.139~\mathrm{kJ} \end{align*}\]
Because the question is asking for “heat evolved/released”, rationalize this to be a positive value. (If the question asked for the change in heat of the water, we could leave this as a negative value).
The plot below gives the vapor pressures of benzene over a range of temperatures. The equation for the linear regression is also given. What is ΔHvap (in kJ mol–1) for benzene?
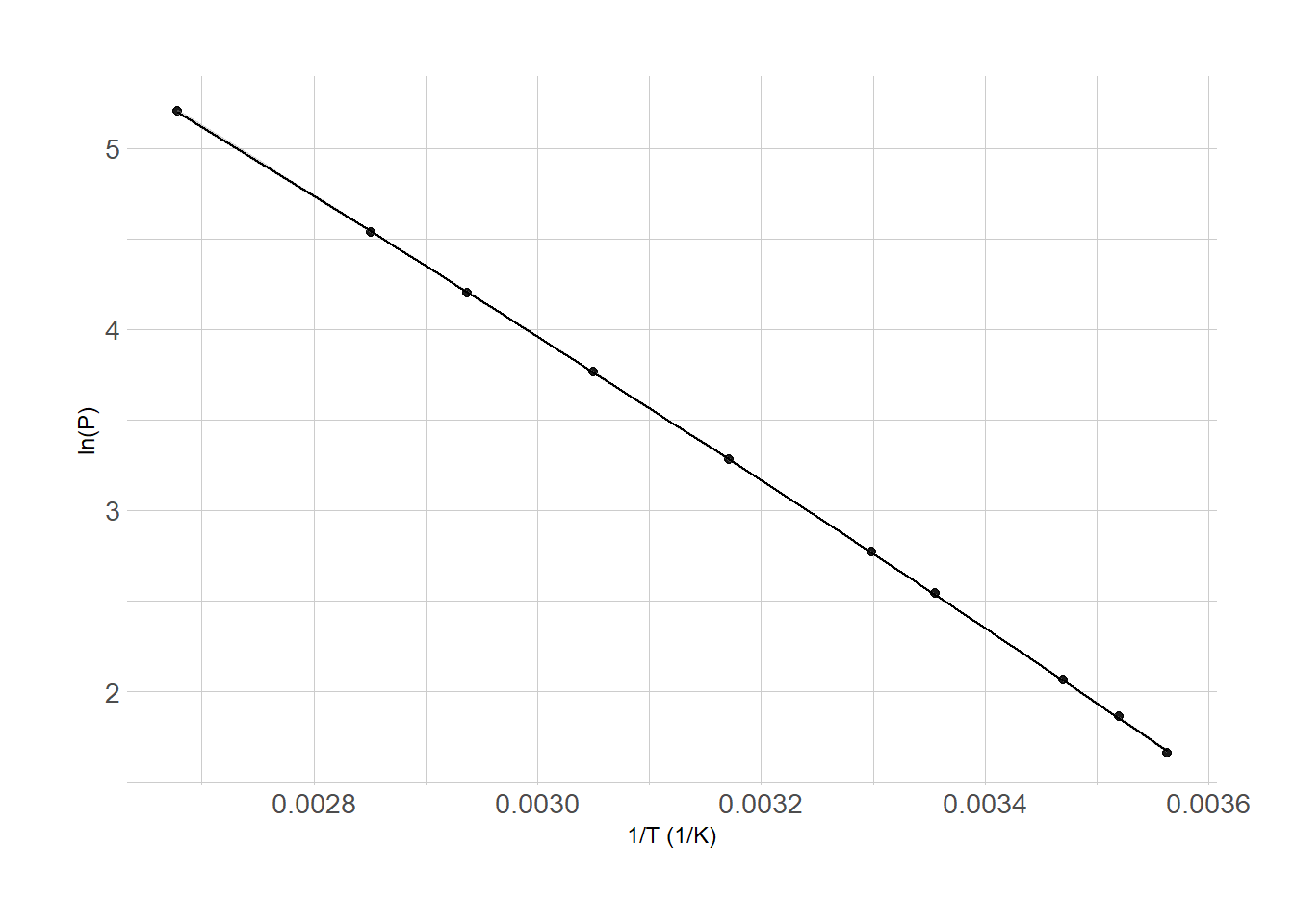
\[y = -4020.5x + 16.014\]
- 15.83
- 33.43
- –8.67
- 54.13
- 28.67
Solution
Answer: B
Concept: Clausius-Clapeyron linear form
Recall that the ln(P) vs 1/T relation gives an approximately straight line whose slope, m, is defined by the heat of vaporization of a substance such that
\[m = -\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R}\]
The slope of the line in the plot is in the given equation for the linear regression. The units of Kelvin are ignored here.
Find Heat of Vaporization
\[\begin{align*} m &= -\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R} \longrightarrow \\[1.5ex] \Delta H &= -m \times R \\[1.5ex] &= -(-4020.5) \left( 8.314~\mathrm{J~mol^{-1}~K^{-1}} \right ) \left ( \dfrac{1~\mathrm{kJ}}{10^3~\mathrm{J}} \right ) \\[1.5ex] &= 33.426~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}} \end{align*}\]
A given solvent has a normal boiling point of 93.7 °C and ΔHvap = 19.3 kJ mol–1. What is the boiling point (in °C) of the solvent when the pressure is 947 mmHg (1.24605 atm)?
- 81.4
- 118.8
- 102.4
- 107
- 94.5
Solution
Answer: D
Concept: Clausius-Clapeyron two-point form
We are provided with two pressures [normal (760 mmHg) and 947 mmHg] as well as one boiling point and a heat of vaporization (ΔHvap). We are asked to solve for the second boiling point. We use the Clausius-Clapeyron two-point form equation.
Identify Variables
ΔHvap = 19.3 kJ mol–1
P1 = 760 mmHg or 1 atm
P2 = 947 mmHg or 1.24605 atm
T1 = 93.7 °C = 366.85 K
T2 = ? °CSolve for T2
\[\begin{align*} \ln \left ( \dfrac{P_2}{P_1} \right ) &= \dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R} \left ( \dfrac{1}{T_1} - \dfrac{1}{T_2} \right ) \longrightarrow \\[1.5ex] T_2 &= \dfrac{1}{\left (-\dfrac{\ln \left ( \dfrac{P_2}{P_1} \right )}{\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R}} + \dfrac{1}{T_1}\right )}\\[1.5ex] &= \dfrac{1}{\left (-\dfrac{\ln \left ( \dfrac{1.24605~\mathrm{atm}}{1~\mathrm{atm}} \right ) } {\dfrac{19.3~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}~K^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{10^3~\mathrm{J}}{1~\mathrm{kJ}}\right )}{8.314~\mathrm{J~mol^{-1}~K^{-1}}}} + \dfrac{1}{366.85~\mathrm{K}}\right ) } - 273.15~\mathrm{K}\\[1.5ex] &= 106.616~\mathrm{K} \end{align*}\]
Math String:
1/((-ln(1.24605/1)/(19.3*1000/8.134))+1/366.85)-273.15Liquid benzene has a vapor pressure of 760 mm Hg and a heat of vaporization of 30.78 kJ mol–1 at 80.0 °C. If the vapor pressure and temperature were plotted for benzene around this temperature using the linear form of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, what would the slope of the resulting line be (to the nearest whole number)?
- –3702
- –4
- –3.7
- 1
- 3700
Solution
Answer: A
Concept: Clausius-Clapeyron linear form
Recall that the ln(P) vs 1/T relation gives an approximately straight line whose slope, m, is defined by the heat of vaporization of a substance such that
\[m = -\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R}\]
We must determine the slope using the given heat of vaporization.
Find the slope
\[\begin{align*} m &= -\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R} \\[1.5ex] &= -\dfrac{30.78~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}} \left ( \dfrac{10^3~\mathrm{J}}{1~\mathrm{kJ}} \right )} {8.314~\mathrm{J~mol^{-1}}} \\[1.5ex] &= -3702.189 \end{align*}\]
Toluene, a common organic solvent, has a heat of vaporization of 38.06 kJ mol–1 and boils at 110.4 °C at sea level. What is the boiling point (in °C) of toluene at the top of Mount Fuji where the atmospheric pressure is only 65% as strong as the pressure at sea level?
- 83
- 88
- 94
- 97
- 104
Solution
Answer: D
Concept: Clausius-Clapeyron two-point form
We are provided with two pressures [normal (1 atm) and 65% of 1 atm (0.65 atm)] as well as one boiling point and a heat of vaporization (ΔHvap). We are asked to solve for the second boiling point. We use the Clausius-Clapeyron two-point form equation.
Identify Variables
ΔHvap = 38.06 kJ mol–1
P1 = 1 atm
P2 = 0.65 atm
T1 = 110.4 °C = 383.55 K
T2 = ? °CSolve for T2
\[\begin{align*} \ln \left ( \dfrac{P_2}{P_1} \right ) &= \dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R} \left ( \dfrac{1}{T_1} - \dfrac{1}{T_2} \right ) \longrightarrow \\[1.5ex] T_2 &= \dfrac{1}{\left (-\dfrac{\ln \left ( \dfrac{P_2}{P_1} \right )}{\dfrac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{vap}}}{R}} + \dfrac{1}{T_1}\right )}\\[1.5ex] &= \dfrac{1}{\left (-\dfrac{\ln \left ( \dfrac{0.65~\mathrm{atm}}{1~\mathrm{atm}} \right ) } {\dfrac{38.06~\mathrm{kJ~mol^{-1}~K^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{10^3~\mathrm{J}}{1~\mathrm{kJ}}\right )}{8.314~\mathrm{J~mol^{-1}~K^{-1}}}} + \dfrac{1}{383.55~\mathrm{K}}\right ) } - 273.15~\mathrm{K}\\[1.5ex] &= 97.318~\mathrm{K} \end{align*}\]
Math String:
1/((-ln(0.65/1)/(38.06*1000/8.134))+1/383.55)-273.15Which of the following unit cells has the lowest packing density?
- primitive cubic
- body-centered cubic
- face-centered cubic
Solution
Answer: A
Concept: Unit cells
A white granular solid melts at 880 °C. It does not conduct electricity unless it is dissolved in water. What type of crystalline solid is it?
- molecular
- ionic
- covalent-network
- metallic
- none of these
Solution
Answer: B
Concept: Properties of solids
What is the coordination number for a simple cubic unit cell?
- 3
- 6
- 8
- 10
- none of these
Solution
Answer: B
Concept: Properties of unit cells